With the explosive growth of connected devices and applications worldwide, the Internet infrastructure is constantly upgrading. One of the most core elements is the IP address protocol (Internet Protocol). The two mainstream versions are IPv4 and IPv6.
Many people have heard of them, but they may not truly understand their structural differences, usage scenarios, and cost advantages. This article will comprehensively compare IPv4 and IPv6 from multiple perspectives, and combine the practical applications of proxies, crawlers, automation, and multi-account management to tell you how to make the right choice.

1. What is IPv4?
IPv4 (Internet Protocol version 4) is the most widely used protocol version. It uses 32-bit addresses and can generate approximately 4.3 billion unique addresses. In the early days of the internet, this number seemed sufficient, but in 2025, with its multi-account, multi-device, and multi-tasking landscape, IPv4 is already a resource shortage.
IPv4 Features
📌 Address length: 32 bits (example: 192.168.0.1)
🌍 Number of available IP addresses: Approximately 4.3 billion
💡 Requires NAT (Network Address Translation)
🔄 Configuration: Manual or DHCP automatic allocation
🔒 Security: Requires additional tools (not natively supported)
💰 Cost: Increasing annually, especially for residential IPv4
IPv4 Use Cases
Maintaining compatibility with legacy systems or applications (most platforms still rely primarily on IPv4)
High-trust tasks: e.g., advertising, account registration, e-commerce operations
When the target website blocks IPv6
2. What is IPv6?
IPv6 (Internet Protocol version 6) is a next-generation protocol designed to address the exhaustion of IPv4 addresses. It uses a 128-bit architecture and can provide 340 undecillion IP addresses, making them virtually unlimited.
IPv6 Features
📌 Address length: 128 bits (example: 2001:0db8:85a3::7334)
🌍 Virtually unlimited addresses
🚫 No NAT required, saving latency and resources
⚙️ Supports stateless auto-configuration
🔒 Native support for the IPsec security protocol
💸 Low cost, suitable for large-scale deployments
IPv6 Application Scenarios
Large-scale data collection (scraping, API requests, SEO)
Automated tasks (RPA) and high-frequency connections
Multi-account isolation (combined with Anti-Detection Browser)
Reduced proxy costs, fast switching between massive IP addresses
⚠️ Note: Not all websites or applications support IPv6. Before purchasing an IPv6 proxy, it is recommended to use the “IPv6 Test Tool” to confirm compatibility with the target platform.
3. IPv4 vs IPv6 comparison table
| Comparison items | IPv4 | IPv6 |
|---|---|---|
| Address length | 32 bits | 128 bits |
| Address format | Decimal (192.168.1.1) | Hexadecimal (2001:db8::1) |
| Available number | Approximately 4.3 billion | 340 trillion trillion |
| NAT support | Required | Not required (native direct connection) |
| Security | Requires additional configuration | Natively supports IPsec |
| Configuration method | Manual / DHCP | Automatic configuration |
| Cost | High, tight supply and demand | Low, can be deployed on a large scale |
| Compatibility | Perfectly compatible with all systems | Gradually becoming popular, some platforms are not fully supported |
4. OKKProxy’s professional advice
As a leading proxy service provider, OKKProxy provides both IPv4 and IPv6 proxy solutions, which can be flexibly selected according to different business scenarios.
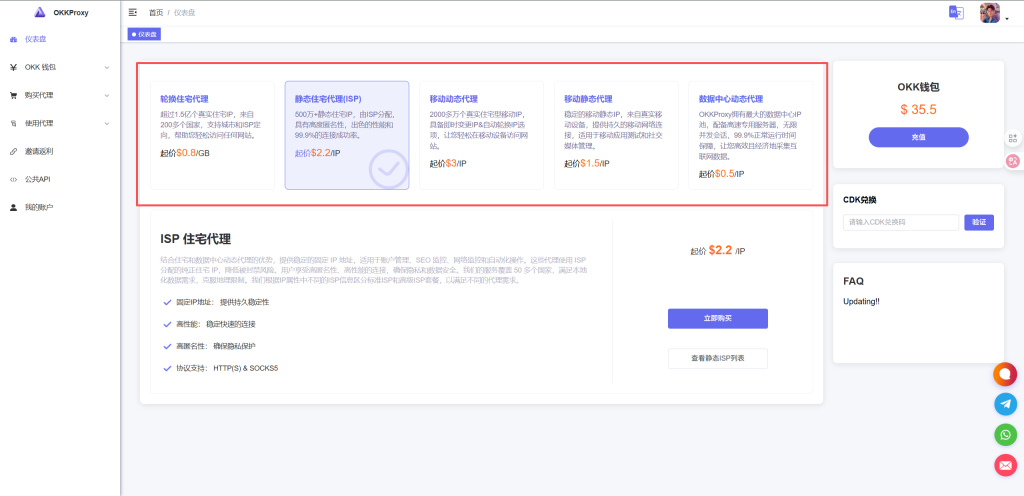
👉 Tasks requiring high trust (account registration, long-term e-commerce operations, social media management): Residential IPv4 is recommended.
👉 Large-scale crawling/API calls/short-term automation tasks: Cost-effective IPv6 proxy is recommended.
Whether it’s cross-border e-commerce, multi-account management, RPA automation, or SEO acquisition, OKKProxy provides you with stable, low-latency, and globally accessible proxy services.
5. Conclusion: IPv6 is the future, but IPv4 remains irreplaceable
IPv6 adoption is accelerating, with more and more websites and services supporting it. However, IPv4 is not obsolete. For residential proxies, cross-border businesses, and some overseas e-commerce and social media platforms, IPv4 remains a necessity.
The best practice is dual-stack support—flexible switching between IPv4 and IPv6, balancing stability, cost, and compatibility, making your network tasks smoother.
🚀 Try OKKProxy Now
Want to know how IPv6 can reduce proxy costs? Or unsure whether your business should use IPv4 or IPv6? **
🎯 Visit the OKKProxy official website now.
Sign up for free and get test traffic instantly to easily handle the network challenges of 2025!
