Quick Answer
When IPs are not rotated during big data collection, websites detect repeated high‑frequency traffic from a single source. This triggers IP bans, rate limiting, CAPTCHA challenges, geographic blocking, and even false data delivery. IP rotation—especially through rotating residential proxies—is essential for scalable and reliable data collection.
Big data collection is the foundation of modern analytics, automation, and competitive intelligence. From ecommerce pricing to search engine monitoring and advertising research, organizations depend on continuous data flows to make informed decisions.
However, one technical mistake silently destroys most large-scale projects: failing to rotate IP addresses.
Within the first minutes of high‑volume crawling, websites detect abnormal request patterns, trigger anti‑bot defenses, and block access. The result is incomplete datasets, misleading information, and wasted infrastructure costs.
This guide explains what happens when IPs are not rotated during big data collection, why websites react aggressively to static traffic, and how proven proxy strategies—based on OKKProxy’s operational experience—restore stability and accuracy.
What Is Big Data Collection?
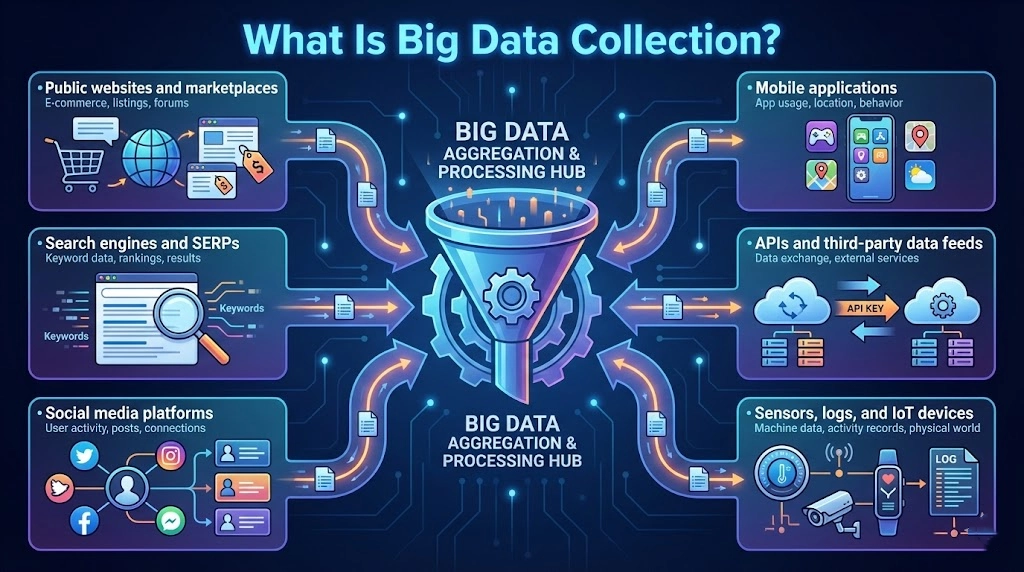
Big data collection refers to gathering extremely large datasets from digital sources for analysis, modeling, or automation.
Typical data sources include:
- Public websites and marketplaces
- Search engines and SERPs
- Social media platforms
- Mobile applications
- APIs and third‑party data feeds
- Sensors, logs, and IoT devices
This explains how big data is collected on the internet and why automation is unavoidable at scale.
How Is Big Data Collected?
Organizations use a combination of technologies to manage volume, velocity, and variety.
Common Big Data Collection Methods
- Web crawling and scraping
- API extraction
- Event tracking
- User behavior analytics
- Data streaming pipelines
All of them generate large numbers of automated requests—precisely what modern websites monitor.
Why Websites Block Big Data Collection Traffic
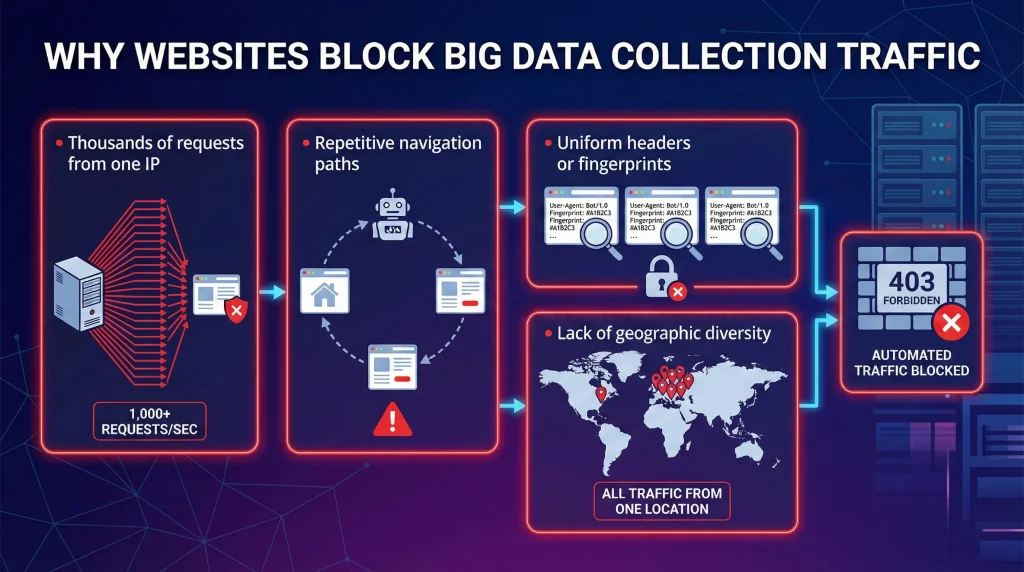
Anti‑scraping systems analyze patterns rather than tools.
Signals that trigger blocking include:
- Thousands of requests from one IP
- Repetitive navigation paths
- Uniform headers or fingerprints
- Lack of geographic diversity
Without IP rotation, traffic appears robotic even when the data itself is public.
7 Powerful Consequences of Not Rotating IPs
1. Immediate IP Bans
Websites quickly blacklist IPs that exceed normal human request rates. Once blocked, all future connections fail.
2. Severe Rate Limiting
Servers may throttle traffic to a few requests per minute, dramatically increasing collection time.
3. CAPTCHA Barriers
reCAPTCHA and behavioral challenges interrupt automated workflows and require costly solving services.
4. Incomplete or Missing Data
Blocked requests lead to partial datasets, destroying analytical accuracy.
5. Fake or Distorted Content
Advanced platforms return empty pages or randomized values to known bot IPs.
6. Geographic Data Loss
Without IP diversity, region‑specific prices, ads, and SERPs remain inaccessible.
7. Long‑Term Infrastructure Blacklisting
Repeated violations can permanently flag your servers or domains.
Why IP Rotation Is Essential for Big Data Collection
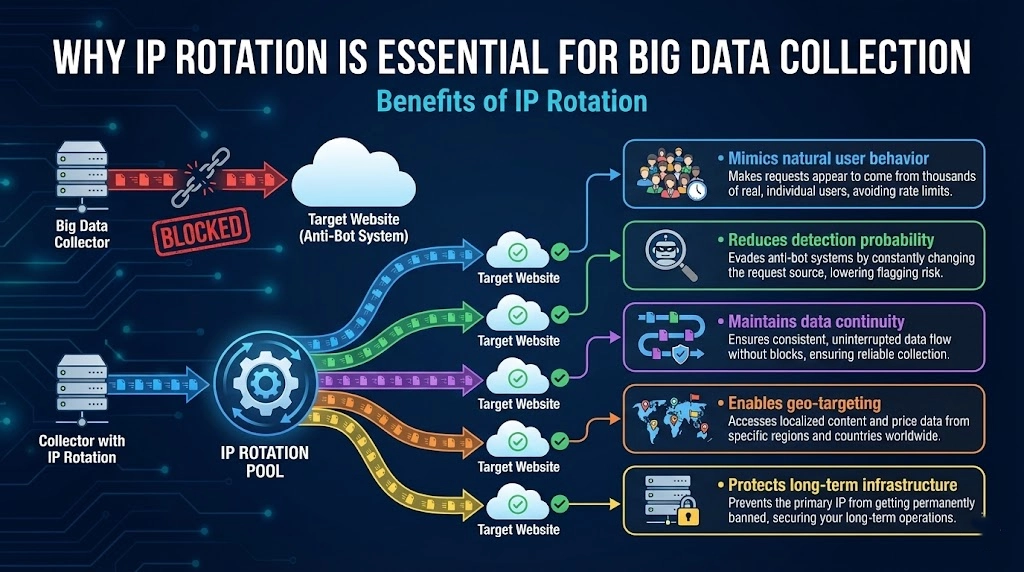
IP rotation distributes requests across many addresses, preventing abnormal traffic concentration.
Benefits of IP Rotation
- Mimics natural user behavior
- Reduces detection probability
- Maintains data continuity
- Enables geo‑targeting
- Protects long‑term infrastructure
This is why IP rotation is considered a core requirement of professional big data collection tools.
Why Rotating Residential Proxies Perform Best
Not all IPs provide equal protection.
| Proxy Type | Detection Risk | Scalability |
| Datacenter proxies | High | Low |
| Static ISP proxies | Medium | Moderate |
| Rotating residential proxies | Low | High |
OKKProxy’s rotating residential proxies use real household IPs supplied by internet service providers worldwide. Each request can be assigned a new IP, closely simulating genuine user traffic.
This approach dramatically improves success rates for:
- Ecommerce price monitoring
- Search result tracking
- Brand protection
- Advertising intelligence
Checklist: Safe Big Data Collection Setup
- Use rotating residential proxies
- Rotate IPs per request or session
- Match IP location with target region
- Control request frequency
- Randomize headers and user agents
- Monitor HTTP errors and CAPTCHAs
- Validate data accuracy continuously
Is Big Data Collection Ethical?
Many users ask: is big data collection ethical?
Ethical data collection depends on:
- Collecting publicly available information
- Avoiding personal identifiable data
- Respecting legal regulations
- Using data responsibly
IP rotation itself does not violate ethics—it simply prevents automated research from being incorrectly blocked.
Frequently Asked Questions
Who Collects Big Data?
Enterprises, researchers, ecommerce platforms, advertisers, and governments all participate in large‑scale data collection.
How Much Big Data Is Being Collected?
Over 300 million terabytes of data are generated daily worldwide, making automation unavoidable.
Should All Organizations Collect and Analyze Big Data?
Pros:
- Better decision‑making
- Market transparency
- Competitive insights
Cons:
- Infrastructure cost
- Compliance complexity
- Technical expertise required
Recommended OKKProxy Resources
- Ecommerce price data collection
- Top rotating residential proxies guide
- Ultimate Guide to Rotating Datacenter Proxies
- Why Your Scraping Scripts Keep Getting Blocked — And How Rotating Residential Proxies Fix It
Final Thoughts
Big data collection fails not because organizations lack tools—but because traffic fails to look human.
Without IP rotation, even the most advanced crawlers collapse under bans, CAPTCHAs, and poisoned data.
By using rotating residential proxies and proven collection frameworks, businesses gain reliable access to global data while maintaining accuracy, compliance, and scalability.
In modern analytics, IP rotation is no longer optional—it is the foundation of successful big data collection.
For more information of big data collection risk, please watch our video on YouTube below:
